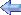
| Sikorsky |
|
S-76 . |
%2016x9.jpg) |
|
Photo: Robert Deering
4/21/2025 Burrard Inlet Vancouver, BC, Canada |
|
The Sikorsky S-76 is a medium-size commercial utility helicopter designed and produced by the American helicopter manufacturer Sikorsky Aircraft. It is the company's first helicopter specifically developed for the civilian market. The S-76 was developed during the mid-1970s, originally being designated S-74 but renamed in honor of the U.S. Bicentennial. Drawing upon its recently-developed S-70 helicopter, it features twin turboshaft engines, four-bladed main and tail rotors, and retractable landing gear. On 13 March 1977, the prototype performed its maiden flight. The initial production variant was the S-76A, the first deliveries of which took place on 27 February 1979. Several improved models were produced over time, including the S-76 Mk II launched in 1982, and the S-76B in 1987. Development of the S-76D was particularly troubled, being delayed by four years due to flight envelope issues; it was finally certified for operation on 12 October 2012. The S-76 initially encountered strong demand from the off-shore oil drilling industry; later on, demand shifted towards the VIP sector of the market. It performed several noteworthy flights, such as the first circumnavigation of the world in an east-to-west direction by a helicopter, and an autonomous demonstration flight during 2016. Sikorsky also used individual helicopters, often heavily modified for the purpose, for experimental purposes and to support other programmes. Demand for the S-76 waned during the 2010s, as newer helicopters such as the AgustaWestland AW139 proved to be stiff competition. During March 2022, Sikorsky halted new orders for the S-76, but stated that it was looking at opportunities for future overseas manufacturing with foreign partners. |
VARIANTS
|
|
General characteristics
Performance
SOURCE: Wikipedia |